Direct vs. Indirect Procurement: Process Optimization Strategies
2024-12-03
In modern supply chain management, procurement plays a crucial role. Procurement methods vary widely, often categorized into direct and indirect procurement based on purpose, needs, and the context of product usage. While both aim to acquire necessary goods or services, their processes, decision-making, and management strategies differ significantly. This article provides a detailed analysis of the differences between direct and indirect procurement and explores how procurement management systems can optimize these processes.
Definitions of Direct and Indirect Procurement
Direct Procurement
Direct procurement refers to the acquisition of raw materials, components, and other essentials required for the production process. These items directly contribute to the production and sales processes. For example, a car manufacturer purchasing steel and engine parts or a food processing company acquiring flour and sugar. Direct procurement is closely tied to a companys core operations and production activities.Indirect Procurement
Unlike direct procurement, indirect procurement involves acquiring supporting goods and services necessary for operational activities. These items do not directly contribute to production but are essential for smooth business operations. Examples include office supplies, IT equipment, employee training services, cleaning services, and logistics. While these items dont impact product manufacturing directly, their quality and efficiency significantly affect overall business performance.Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Procurement
1、Purpose
● Direct Procurement: Supports the production process, ensuring the production line operates smoothly.● Indirect Procurement: Facilitates daily operations, enhancing management and service capabilities.
For instance, a car manufacturer purchasing steel or engine parts is an example of direct procurement, whereas acquiring office computers or employee training programs falls under indirect procurement.
2、Nature of Items
● Direct Procurement: Involves production materials that impact product quality, cost, and production timelines. These are often high-volume, frequently purchased items.● Indirect Procurement: Comprises consumables or services that influence daily operations without directly affecting product quality or production schedules. Purchases are typically smaller and less frequent.
3、Processes
● Direct Procurement: Requires strict process control and budget management due to its critical role in production. Close collaboration between procurement, production, and R&D teams is essential to ensure compatibility with production requirements.● Indirect Procurement: Features simpler processes, often relying on bulk purchasing or standardized procedures to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
4、Supplier Management
● Direct Procurement: Relies on long-term strategic partnerships with suppliers, emphasizing quality control, delivery timelines, and after-sales service. This requires robust supplier relationships and complex management practices.● Indirect Procurement: Simpler supplier management, often involving multiple vendors to ensure diversity and flexibility in supply.
5、Cost Control
● Direct Procurement: Critical to cost management as it directly affects production costs and product pricing. Emphasis is placed on cost optimization, bulk purchasing, and negotiation with suppliers.● Indirect Procurement: While cost control is also important, it typically involves simplifying processes and standardization to minimize expenses.
Role of Procurement Management Systems (PMS)
Procurement management systems (PMS) are essential tools for modern businesses, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling precise management. For both direct and indirect procurement, PMS offers the following advantages:1、Process Automation
PMS automates procurement workflows, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency. From generating purchase orders to tracking progress, automation minimizes errors and shortens procurement cycles.
2、Data Analysis and Decision Support
By consolidating procurement data, PMS provides detailed reports and analyses to refine procurement strategies. For direct procurement, it tracks material trends and supplier performance; for indirect procurement, it monitors usage frequency and inventory levels, offering actionable insights for decision-making.3、Supplier Management
PMS streamlines supplier management, evaluating performance metrics like quality and delivery in direct procurement, while enabling easy price and service comparisons for indirect procurement.
4、Cost and Budget Management
PMS helps set procurement budgets and monitors expenditures in real-time, preventing overruns. For direct procurement, it manages bulk purchases; for indirect procurement, it optimizes low-cost, high-efficiency strategies.5、Contract Management and Compliance
PMS ensures contract terms are upheld and reduces legal risks. In direct procurement, this safeguards against supply chain disruptions, while for indirect procurement, it ensures service quality and timely delivery.
Choosing the Right Procurement Management System
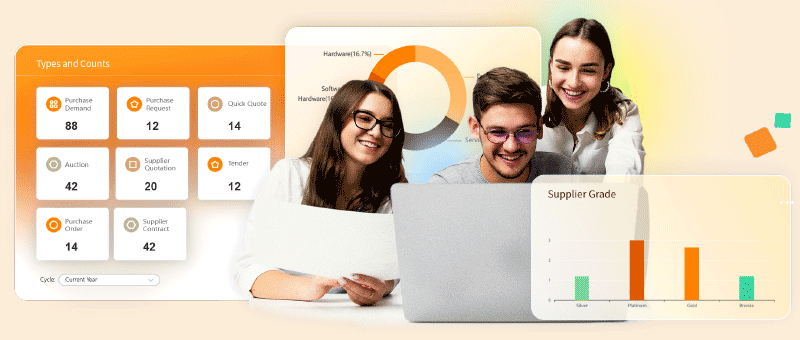
When selecting a PMS, consider factors like comprehensive functionality, ease of use, integration capabilities, data analysis, security, and cost-effectiveness. An ideal PMS should enhance supplier management, order workflows, inventory control, and contract oversight while offering robust data insights for informed decision-making.8Manage SRM, for instance, is a versatile solution offering extensive procurement management features and seamless integration with other systems. Its user-friendly interface, scalability, and powerful data analytics make it a preferred choice for many businesses. By facilitating intelligent procurement management and streamlining supply chain operations, 8Manage SRM supports both SMEs and large enterprises effectively.
FAQs
1、Which is more important for businesses, direct or indirect procurement?
Both are vital for business operations. Direct procurement ensures uninterrupted production, while indirect procurement supports smooth daily operations. Companies should allocate resources wisely to optimize both procurement strategies.2、How can a PMS help control costs?
PMS provides data analysis, automated workflows, and budget controls to optimize procurement expenses. It tracks trends, evaluates suppliers, and monitors budgets in real-time, enabling precise decisions and avoiding unnecessary spending.3、How do I choose the best PMS for my company?
Evaluate your company’s size, procurement needs, and the system’s scalability. Essential features include order and supplier management, budget control, ease of integration with existing systems (e.g., ERP, finance), and responsive support services.


What Are the Main Risks in Projects, and How to Manage Them Effectively?
Are your project managers ready for AI?